11.2 Being a Professional of Integrity
Whenever you think about the behaviour you expect of yourself in your personal life and as a professional, you are engaging in a philosophical dialogue with yourself to establish the standards of behaviour you choose to uphold, that is, your ethics. You may decide you should always tell the truth to family, friends, customers, clients, and shareholders, and if that is not possible, you should have very good reasons why you cannot. You may also choose never to defraud or mislead your business partners. You may decide, as well, that while you are pursuing profit in your business, you will not require that all the money on the table come your way. Instead, there might be some to go around to those who are important because they are affected one way or another by your business. These are your stakeholders.
Acting with Integrity
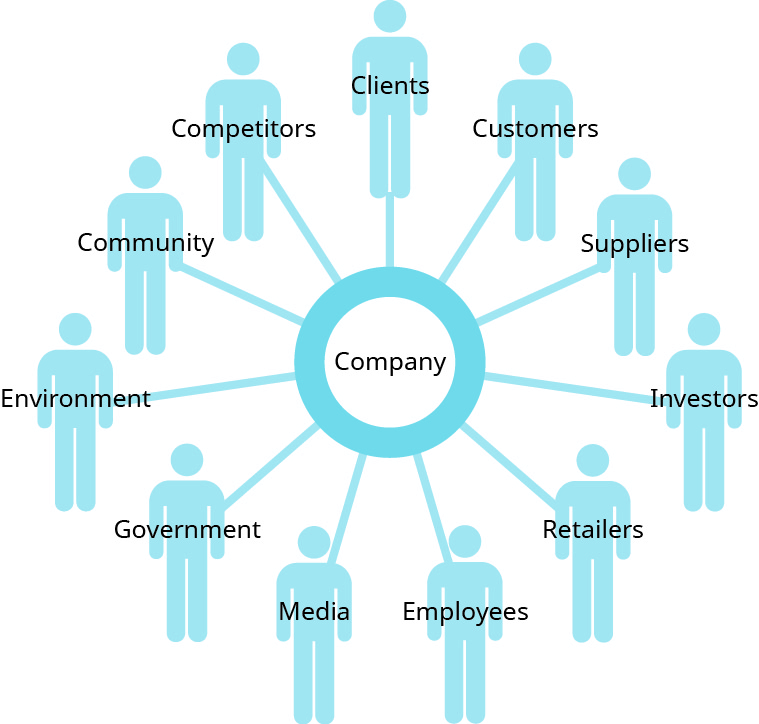
Clients, customers, suppliers, investors, retailers, employees, the media, the government, members of the surrounding community, competitors, and even the environment are stakeholders in a business; that is, they are individuals and entities affected by the business’s decisions (Figure 11.1: A Company’s Stakeholders). Stakeholders typically value a leadership team that chooses the ethical way to accomplish the company’s legitimate for-profit goals. For example, Patagonia expresses its commitment to environmentalism via its “1% for the Planet” program, which donates 1 percent of all sales to help save the planet. In part because of this program, Patagonia has become a market leader in outdoor gear.
Stakeholders are the individuals and entities affected by a business’s decisions, including clients, customers, suppliers, investors, retailers, employees, the media, the government, members of the surrounding community, the environment, and even competitors. (attribution: Copyright Rice University, OpenStax, under CC BY 4.0 license)
Being successful at work may therefore consist of much more than simply earning money and promotions. It may also mean treating our employees, customers, and clients with honesty and respect. It may come from the sense of pride we feel about engaging in honest transactions, not just because the law demands it but because we demand it of ourselves. It may lie in knowing the profit we make does not come from shortchanging others. Thus, business ethics guides the conduct by which companies and their agents abide by the law and respect the rights of their stakeholders, particularly their customers, clients, employees, and the surrounding community and environment. Ethical business conduct permits us to sleep well at night.
Are business ethics an oxymoron? Read “Why Ethics Matter” to understand just a few of the reasons to have values-driven management.
Nearly all systems of religious belief stress the building blocks of engaging others with respect, empathy, and honesty. These foundational beliefs, in turn, prepare us for the codes of ethical behaviour that serve as ideal guides for business and the professions. Still, we need not subscribe to any religious faith to hold that ethical behaviour in business is still necessary. Just by virtue of being human, we all share obligations to one another, and principal among these is the requirement that we treat others with fairness and dignity, including in our commercial transactions.
For this reason, we use the words ethics and morals interchangeably in this book, though some philosophers distinguish between them. We hold that “an ethical person” conveys the same sense as “a moral person,” and we do not regard religious belief as a requirement for acting ethically in business and the professions. Because we are all humans and in the same world, we should extend the same behaviour to all. It is the right way to behave, but it also burnishes our own professional reputation as business leaders of integrity.
Integrity—that is, unity between what we say and what we do—is a highly valued trait. But it is more than just consistency of character. Acting with integrity means we adhere strongly to a code of ethics, so it implies trustworthiness and incorruptibility. Being a professional of integrity means consistently striving to be the best person you can be in all your interactions with others. It means you practice what you preach, walk the talk, and do what you believe is right based upon reason. Integrity in business brings many advantages, not the least of which is that it is a critical factor in allowing business and society to function properly.
Successful corporate leaders and the companies they represent will take pride in their enterprise if they engage in business with honesty and fair play. To treat customers, clients, employees, and all those affected by a firm with dignity and respect is ethical. In addition, laudable business practices serve the long-term interests of corporations. Why? Because customers, clients, employees, and society at large will much more willingly patronize a business and work hard on its behalf if that business is perceived as caring about the community it serves. And what type of firm has long-term customers and employees? One whose track record gives evidence of honest business practice.
In this interview, Mark Faris, a white-collar criminal convicted of fraud, claims that greed, arrogance, and ambition were motivating factors in his actions. He also discusses the human ability to rationalize our behaviour to justify it to ourselves. Note his proposed solutions: practicing ethical leadership and developing awareness at an individual level via corporate training.
Many people confuse legal and ethical compliance. They are, however, totally different and call for different standards of behaviour. The concepts are not interchangeable in any sense of the word. The law is needed to establish and maintain a functioning society. Without it, our society would be in chaos. Compliance with these legal standards is strictly mandatory: If we violate these standards, we are subject to punishment as established by the law. Therefore, compliance in terms of business ethics generally refers to the extent to which a company conducts its business operations in accordance with applicable regulations, statutes, and laws. Yet this represents only a baseline minimum. Ethical observance builds on this baseline and reveals the principles of an individual business leader or a specific organization. Ethical acts are generally considered voluntary and personal—often based on our perception of or stand on right and wrong.
Some professions, such as medicine and the law, have traditional codes of ethics. The Hippocratic Oath, for example, is embraced by most professionals in health care today as an appropriate standard always owed to patients by physicians, nurses, and others in the field. This obligation traces its lineage to ancient Greece and the physician Hippocrates. Business is different in not having a mutually shared standard of ethics. This is changing, however, as evidenced by the array of codes of conduct and mission statements many companies have adopted over the past century. These have many points in common, and their shared content may eventually produce a code universally claimed by business practitioners. What central point might constitute such a code? Essentially, a commitment to treat with honesty and integrity customers, clients, employees, and others affiliated with a business.
The law is typically indebted to tradition and precedence, and compelling reasons are needed to support any change. Ethical reasoning often is more topical and reflects the changes in consciousness that individuals and society undergo. Often, ethical thought precedes and sets the stage for changes in the law.
Behaving ethically requires that we meet the mandatory standards of the law, but that is not enough. For example, an action may be legal that we personally consider unacceptable. Companies today need to be focused not only on complying with the letter of the law but also on going above and beyond that basic mandatory requirement to consider their stakeholders and do what is right.
To see an example of a corporate ethical code or mission statement, visit Johnson & Johnson and read “Our Credo” written by former chair Robert Wood Johnson.
Forbes provides an annual list of companies recently deemed the most ethical according to their standards and research.
Ends, Means, and Character in Business
How, then, should we behave? Philosophy and science help us answer this question. From philosophy, three different perspectives help us assess whether our decisions are ethical on the basis of reason. These perspectives are called normative ethical theories and focus on how people ought to behave, and we’ll discuss them in this chapter. In contrast, descriptive ethical theories are based on scientific evidence, primarily in the field of psychology, and describe how people tend to behave within a particular context; however, they are not the subject of this book.
The first normative approach is to examine the ends, or consequences, a decision produces in order to evaluate whether those ends are ethical. Variations on this approach include utilitarianism, teleology, and consequentialism. For example, utilitarianism suggests that an ethical action is one whose consequence achieves the greatest good for the greatest number of people. So if we want to make an ethical decision, we should ask ourselves who is helped and who is harmed by it. Focusing on consequences in this way generally does not require us to take into account the means of achieving that particular end, however. That fact leads us to the second normative theory about what constitutes ethical conduct.
The second approach does examine the means, or actions, we use to carry out a business decision. An example of this approach is deontology, which essentially suggests that it is the means that lend nobility to the ends. Deontology contends that each of us owes certain duties to others (deon is a Greek word for duty or obligation) and that certain universal rules apply to every situation and bind us to these duties. In this view, whether our actions are ethical depends only on whether we adhere to these rules. Thus, the means we use are the primary determinants of ethical conduct. The thinker most closely associated with deontology is the eighteenth-century German philosopher Immanuel Kant (Figure 11.2: Immanuel Kant and Kantianism). Immanuel Kant was an eighteenth-century philosopher, now associated with deontology, who spent nearly all his professional life teaching at the university in Königsberg (which today is Kaliningrad, the westernmost point in Russia). (credit right: modification of “Kant foto” by “Becker”/Wikimedia Commons, Public Domain)

The third normative approach, typically called virtue theory, focuses on the character of the decision-maker—a character that reflects the training we receive growing up. In this view, our ethical analysis of a decision is intimately connected with the person we choose to be. It is through the development of habits, the routine actions in which we choose to engage, that we are able to create a character of integrity and make ethical decisions. Put differently, if a two-year-old is taught to take care of and return borrowed toys even though this runs contrary to every instinct they have, they may continue to perfect their ethical behaviour so that at age forty, they can be counted on to safeguard the tens of millions of dollars investors have entrusted to their care in brokerages.
Virtue theory has its roots in the Greek philosophical tradition, whose followers sought to learn how to live a flourishing life through study, teaching, and practice. The cardinal virtues to be practiced were courage, self-control, justice, and wisdom. Socrates was often cited as a sage and a role model, whose conduct in life was held in high regard.
Aristotle and the Concept of Phronesis, or Practical Wisdom
Phrónēsis (fro-NEE-sis) is a type of practical wisdom that enables us to act virtuously. In “The Big Idea: The Wise Leader,” a Harvard Business Review article on leadership and ethical decision-making, Ikujiro Nonaka, a Japanese organizational theorist, and Hirotaka Takeuchi, a professor of Management Practice at Harvard Business School, discusses the gap between the theory and practice of ethics and which characteristics make a wise leader.
The authors conclude that “the use of explicit and tacit knowledge isn’t enough; chief executive officers (CEOs) must also draw on a third, often forgotten kind of knowledge, called practical wisdom. Practical wisdom is tacit knowledge acquired from experience that enables people to make prudent judgments and take actions based on the actual situation, guided by values and morals.”
The concept of practical wisdom dates back to Aristotle, who considered phronesis, which can also be defined as prudence, to be a key intellectual virtue. Phronesis enables people to make ethically sound judgments. According to the authors, phronetic leaders:
- Practice moral discernment in every situation, making judgments for the common good that are guided by their individual values and ethics;
- Quickly assess situations and envision the consequences of possible actions or responses;
- Create a shared sense of purpose among executives and employees and inspire people to work together in pursuit of a common goal;
- Engage as many people as possible in conversation and communicate using metaphors, stories, and other figurative language in a way that everyone can understand; and
- Encourage practical wisdom in others and support the training of employees at all levels in its use.
In essence, the first question any company should ask itself is: “Do we have a moral purpose?” Having a moral purpose requires focusing on the common good, which precedes the accumulation of profit and results in economic and social benefits. If companies seek the common good, profits generally will follow.
Integrating Ethics into AI Business Strategies
Did you know that AI (artificial intelligence) systems can inadvertently perpetuate biases present in their training data, leading to unfair treatment of certain groups? This is just one of the many ethical challenges that businesses must address when integrating AI into their operations.
As we integrate artificial intelligence into various sectors we must navigate the complex terrain of ethics to ensure that these powerful tools are used responsibly.
Strategies for Ethical AI Use
- Developing Ethical Guidelines: Organizations should create comprehensive ethical guidelines for AI use that align with their values and mission.
- Inclusive Design: AI tools should be designed with input from a diverse group of stakeholders.
- Bias Mitigation: Regular audits and updates should be conducted to identify and mitigate biases in AI systems.
- Data Governance: Establish clear policies for data collection, storage, and usage that comply with privacy laws and ethical standards.
- Continuous Education: Offer workshops and training for faculty on the ethical implications of AI.
Challenges in Upholding AI Ethics
Despite best efforts, challenges persist in maintaining ethical standards:
- Complexity of AI Systems: The intricate nature of AI algorithms can make transparency difficult to achieve.
- Rapid Technological Change: The development of AI often outpaces the creation of ethical guidelines and regulations.
- Diverse Cultural Perspectives: Global institutions must navigate varying cultural norms and values related to AI ethics.
Real-world examples of why it’s important to have ethical AI
- Scrutinizing Bias and Fairness: AI systems are only as unbiased as the data they are trained on. For instance, Amazon had to scrap an AI recruiting tool (Link opens in a new tab) because it showed bias against women. The algorithm had learned from historical hiring data, which was skewed toward male candidates. Businesses must critically examine datasets for biases and understand the implications of deploying biased AI systems in real-world scenarios.
- Data Privacy and Security: With great power comes great responsibility. The Cambridge Analytica scandal (Link opens in a new tab) is a stark reminder of how data can be misused. AI systems often require vast amounts of data, which can include sensitive personal information. Businesses have to instill in employees a strong understanding of data privacy laws, such as the General Data Protection Regulation, and the ethical handling of data.
- AI Transparency and Explainability: AI can sometimes be a black box, making decisions that even its creators can’t fully explain. The European Union’s GDPR (Link opens in a new tab) introduced the right to explanation, where individuals can ask for the rationale behind an AI decision that affects them. Businesses should highlight the importance of developing transparent AI systems that stakeholders can trust and understand.
- Global Ethical Standards: Ethical AI usage doesn’t have a one-size-fits-all solution, as cultural norms vary widely. For example, China’s social credit system, (Link opens in a new tab) which uses AI to monitor citizens’ behaviour, may be seen as a severe privacy invasion in other countries. Businesses need to prepare employees to navigate the complex global landscape of AI ethics.
- Stakeholder Impact and Responsibility: The deployment of AI can have far-reaching impacts on employees, customers, and society at large. When Microsoft’s chatbot Tay (Link opens in a new tab) was released on Twitter, it quickly learned to spout offensive language from interactions with users. Businesses must teach employees to consider the broader societal implications of AI and their responsibility towards all stakeholders.
- Responsible Innovation: Innovation should not come at the cost of ethical considerations. Google’s Project Maven, (Link opens in a new tab) which aimed to improve drone strike accuracy using AI, raised ethical concerns when utilizing Google’s expertise for military projects which potentially put humans in danger. Eventually, this led to employee resignations. Businesses must understand that responsible innovation involves weighing the benefits of AI against potential ethical and moral costs.
Summary
Ethics sets the standards that govern our personal and professional behaviour. To conduct business ethically, we must choose to be a professional of integrity. The first steps are to ask ourselves how we define success and to understand that integrity calls on us to act in a way that is consistent with our words. There is a distinct difference between legal compliance and ethical responsibility, and the law does not fully address all ethical dilemmas that businesses face. Sound ethical practice meets the company’s culture, mission, or policies above and beyond legal responsibilities. The three normative theories of ethical behaviour allow us to apply reason to business decisions as we examine the result (utilitarianism), the means of achieving it (deontology), and whether our choice will help us develop a virtuous character (virtue ethics).

