4.1 The Globalization of Business
Do you wear Nike shoes or Timberland boots? Listen to Billie Eilish, Drake, Taylor Swift, or BTS on Spotify? If you answered yes to either of these questions, you’re a global business customer. Both Nike and Timberland manufacture most of their products overseas. Spotify is a Swedish enterprise.

Take an imaginary walk down Orchard Road, the most fashionable shopping area in Singapore. You’ll pass department stores such as Tokyo-based Takashimaya and London’s very British Marks & Spencer, both filled with well-known international labels such as Ralph Lauren Polo, Burberry, and Chanel. If you need a break, you can also stop for a latte at Seattle-based Starbucks.
When you’re in the Chinese capital of Beijing, don’t miss Tiananmen Square. Parked in front of the Great Hall of the People, the seat of Chinese government, are fleets of black Buicks, cars made by General Motors in Flint, Michigan. If you’re adventurous enough to find yourself in Faisalabad, a medium-size city in Pakistan, you’ll see Hamdard University, located in a refurbished hotel. Step inside its computer labs, and the sensation of being in a faraway place will likely disappear: on the computer screens, you’ll recognize the familiar Microsoft flag—the same one emblazoned on screens in Microsoft’s hometown of Seattle and just about everywhere else on the planet.
The globalization of business is bound to affect you. Not only will you buy products manufactured overseas, but it’s likely that you’ll meet and work with individuals from various countries and cultures as customers, suppliers, colleagues, employees, or employers. The bottom line is that the globalization of world commerce has an impact on all of us – evidenced in the figure below, The Expanded Circular Flow Model. Therefore, it makes sense to learn more about how globalization works.
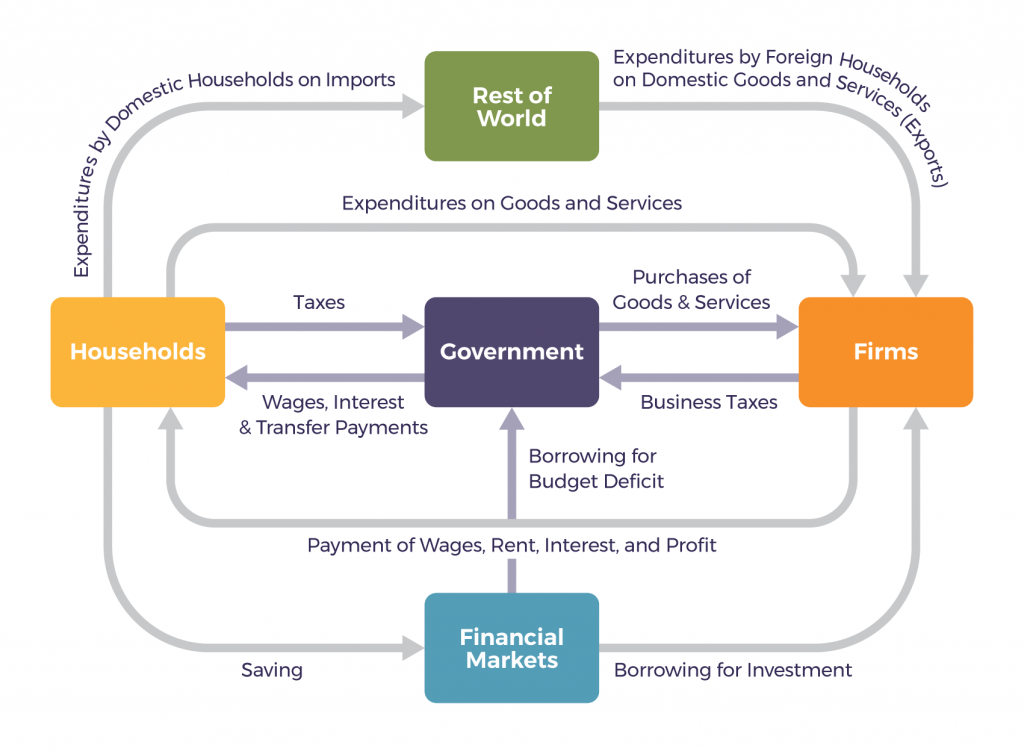
Never before has business spanned the globe the way it does today and will continue to do in the future. But why is international business important? Why do companies and nations engage in international trade? What strategies do they employ in the global marketplace? How do governments and international agencies promote and regulate international trade? These questions and others will be addressed in this chapter. Let’s start by looking at the more specific reasons why companies and nations engage in international trade.

