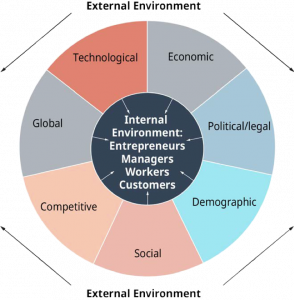
2.1 The Organizational Boundaries and Environments
Businesses do not operate in a vacuum but rather in a dynamic environment that has a direct influence on how they operate and whether they will achieve their objectives. This external business environment is composed of numerous outside organizations and forces that we can group into seven key subenvironments, as Figure 2.1 illustrates: economic, political and legal, demographic, social, competitive, global, and technological. Each of these sectors creates a unique set of challenges and opportunities for businesses.
Business owners and managers have a great deal of control over the internal environment of business, which covers day-to-day decisions. They choose the supplies they purchase, which employees they hire, the products they sell, and where they sell those products. They use their skills and resources to create goods and services that will satisfy existing and prospective customers. However, the external environmental conditions that affect a business are generally beyond the control of management and change constantly. To compete successfully, business owners and managers must continuously study the environment and adapt their businesses accordingly.
Other forces, such as natural disasters, can also have a major impact on businesses. While still in the rebuilding stage after Hurricane Katrina hit in 2005, the U.S. Gulf Coast suffered another disaster in April 2010 as a result of an explosion on the Deepwater Horizon oil-rig, which killed 11 workers and sent more than 3 million barrels of oil into the Gulf of Mexico. This event, which played out for more than 87 days, severely affected the environment, businesses, tourism, and people’s livelihoods. Global oil conglomerate BP, which was responsible for the oil spill, has spent more than $60 billion in response to the disaster and cleanup. Fourteen years after the explosion, tourism and other businesses are slowly recovering. Scientists continue to conduct environmental assessments to understand and mitigate the long-term consequences of the oil spill.